Printer-Friendly PDF
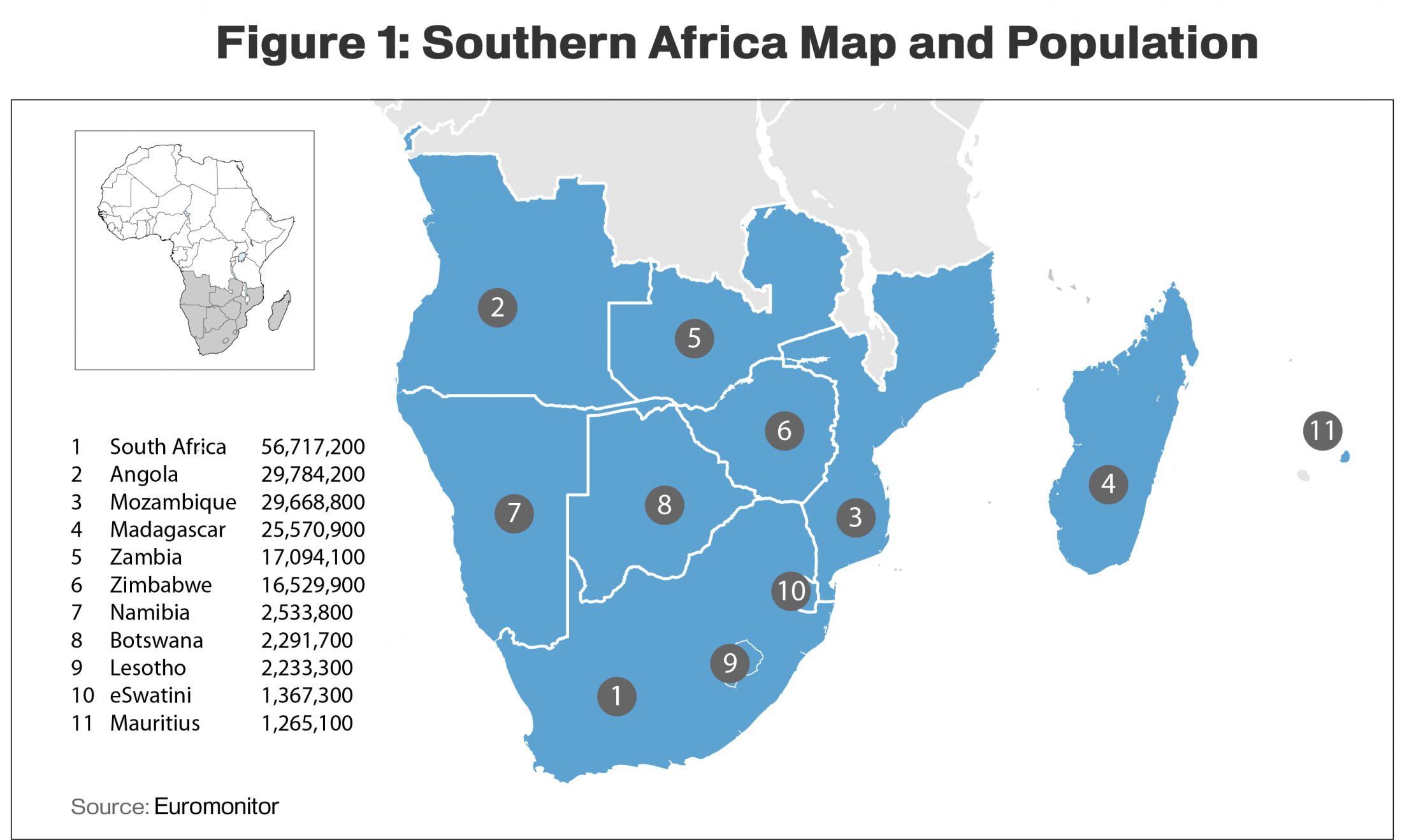
Two-way agricultural trade between the United States and Southern Africa has grown significantly in the past decade, reaching a record $1.5 billion in 2017. The region imported $14 billion in agricultural and related products last year and the potential for U.S. export growth is strong, given that many of these are products that the United States produces competitively. USDA’s Foreign Agricultural Service (FAS) defines the Southern Africa region as the countries of Angola, Botswana, Lesotho, Madagascar, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, eSwatini (formerly Swaziland), Zambia, and Zimbabwe. The region is home to 167 million people.
Demographic and Consumption Trends
Among the countries in Southern Africa, the World Bank classifies Angola, Botswana, Mauritius, Namibia, and South Africa as upper middle-income economies with per capita income of between $4,408 and $9,794. Lesotho, eSwatini, Zambia, and Zimbabwe are classified as lower middle-income economies, while Madagascar and Mozambique are classified as low-income economies. The World Bank estimates average annual population growth in Sub-Saharan Africa, of which Southern Africa is a part, at 2.7 percent, with real GDP growth for the region at 2.6 percent. South Africa and Angola, the two strongest economies of the Southern Africa region, are projected to experience increased overall economic growth in 2018, as the business environment improves. A growing middle class and large scale rural-to-urban migration have created strong demand for diverse agricultural products across Sub-Saharan Africa, resulting in the growth of imports over the past decade. These factors combine to create an exciting opportunity for U.S. agricultural exporters.
Global Market Perspective
Southern Africa is typically a net importer of agricultural products. In recent years imports have been largely driven by demand for diverse food and agricultural products and the changing tastes and preferences of a more connected, global society. Increased urbanization is driving demand for convenient and ready-to-eat foods. As a result, the number of restaurants, bars, and cafes (including U.S. and local fast food chains) is growing as dining out becomes more popular throughout the region, especially in South Africa.
U.S. Exports to Southern Africa
U.S. agricultural exports to Southern Africa have fluctuated over the past 10 years between $372 million and $766 million. This fluctuation is caused primarily by drought-related variations in local corn production and competition from other wheat suppliers. South Africa and Angola are the largest importers of U.S. agricultural products in the region, accounting for 90 percent of U.S.-origin imports in 2017. South Africa serves as a gateway for distribution throughout the region and U.S. products may be transshipped to neighboring countries. U.S. agricultural exports to Southern Africa totaled $627 million in 2017, accounting for only 4 percent of the region’s $14 billion in total imports.
U.S. Agricultural Exports to Southern Africa
Country
Values in Million USD
2008
2009
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
South Africa
447
198
333
402
302
333
288
242
354
398
Angola
144
80
174
230
268
271
299
130
97
169
Mozambique
50
43
45
74
51
34
19
10
26
32
Namibia
8
5
3
18
10
10
4
9
10
8
Madagascar
10
4
14
12
11
4
0*
4
11
7
Mauritius
13
2
3
6
6
7
5
4
4
5
eSwatini
3
3
5
2
7
7
9
5
6
5
Zimbabwe
40
37
8
12
5
1
5
5
9
3
Zambia
4
1
1
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
Botswana
0*
0*
0*
0*
1
1
0*
0*
0*
0*
Lesotho
0*
0*
0*
7
14
0*
0*
0*
1
0*
Total Agricultural Exports
720
372
587
766
676
670
630
411
519
627
Source: USDA-FAS GATS/U.S. Census Bureau – BICO HS-10, * = less than $1 million
U.S. Exports, Market Share, and the Policy Landscape
Top U.S. Exports of Agricultural Products to Southern Africa
Product
Values in Millions USD
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
Poultry Meat & Products (ex. eggs)
263
283
113
114
249
Wheat
36
17
20
56
45
Corn
0.2
0.3
0.1
48
39
Planting Seeds
24
22
20
22
25
Tree Nuts
20
25
23
20
22
Dairy Products
30
18
15
14
18
Prepared Food
28
19
19
22
18
Forest Products
18
18
19
19
16
Beef & Beef Products
15
17
8
6
15
Feeds & Fodders
11
9
12
17
14
Total Agricultural Products
670
630
411
518
627
Source: USDA FAS GATS/U.S. Census Bureau, BICO HS-10
For the last five years, poultry meat and products (excluding eggs) have topped the list of U.S. agricultural exports to Southern Africa, with sales primarily to South Africa and Angola. Exports of chicken legs to South Africa have fared well despite a quota of 65,000 tons (at the most-favored-nation tariff rate of 37 percent) and prohibitively high anti-dumping tariff rates above the quota. In May 2018, Namibia opened its market to U.S. poultry and FAS projects that Namibian broiler meat imports could increase by about 3.5 percent this year, reaching approximately 30,500 tons in 2018, driven by local demand that cannot adequately be met by local supply. Broiler meat is relatively affordable and is becoming an increasingly important protein source in the diet of many Namibians.
Another new opportunity in the region is the opening of South Africa to imports of U.S. table and hatching eggs. While South Africa was previously self-sufficient in egg production, the local egg industry is now recovering from highly pathogenic avian influenza (H5N8) outbreaks in 2017. FAS projects that South African table egg imports could reach 75 tons in 2018. There are also opportunities for hatching eggs as a result of the H5N8 outbreaks. However, South African government officials have informed FAS that the opening of the hatching egg market will likely be a temporary concession.
As noted earlier, the demand for U.S. corn and wheat is highly dependent on domestic supplies and global prices. The 2016/2017 marketing year saw U.S. wheat at highly competitive prices due to problems with the European crop, but recently wheat from countries in the Black Sea region has proven very competitive. Strong U.S. corn exports in 2016 and 2017 were a result of drought conditions in the Sub-Saharan Africa region and demand for U.S. corn is expected to revert to pre-2016 levels as domestic yields rebound. While U.S. exports of planting seeds, tree nuts, prepared foods, forest products, and feeds and fodder have remained steady over the last five years, there is ample opportunity to capture market share from international competitors.
Free Trade Agreements
In 2017, the United States provided only 4 percent of Southern Africa’s agricultural imports. Major competitors for market share are the European Union with 27 percent, followed by African countries with 26 percent, Asian countries with 24 percent, and the Mercosur countries with 13 percent. This can be explained in part by the preferential trade relationships and free trade agreements that the region has with the EU, other African countries, and Mercosur. The United States does not have a free trade agreement with the region. While Asian countries do not have a free trade agreement either, they have a comparative advantage in the production of rice and palm oil.
Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) in Southern Africa
Active FTA
Participating Southern African Countries
Southern African Customs Union (SACU)
Botswana, Lesotho, Namibia, South Africa, eSwatini
SACU and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) – Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland
Botswana, Lesotho, Namibia, South Africa, eSwatini
SACU-Southern Common Market (Mercosur) Preferential Trade Agreement
Botswana, Lesotho, Namibia, South Africa, eSwatini
Southern African Development Community (SADC) Protocol on Trade
Angola, Botswana, Lesotho, Madagascar, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, eSwatini, Zambia, Zimbabwe
SADC & European Union Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA)
Botswana, Lesotho, Namibia, South Africa, eSwatini, Mozambique
Common Market for Southern and Eastern Africa (COMESA)
Madagascar, Mauritius, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe/South Africa bilateral trade agreement
South Africa, Zimbabwe
Mauritius and Madagascar FTA
Madagascar, Mauritius
Mauritius and Turkey FTA
Mauritius
Mauritius – Pakistan Preferential Trade Agreement
Mauritius
FTA in Negotiations
Participating Southern African Countries
SACU – India Preferential Trade Agreement
Botswana, Lesotho, Namibia, South Africa, eSwatini
SADC – East Africa Community – COMESA Tripartite Free Trade Agreement
Angola, Botswana, Lesotho, Madagascar, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, eSwatini, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Africa Continental Free Trade Agreement (ACFTA)
Angola, Botswana, Lesotho, Madagascar, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, eSwatini, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Source: WTO Trade Agreement databases
Opportunities for U.S. Ag Exporters
Potential Opportunities for U.S. Exporters
Product
Southern African Countries
Almonds
eSwatini, Angola, Botswana, Lesotho, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Zambia
Animal Feed
Botswana, Namibia, South Africa, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Apples
Madagascar, Mauritius
Beef
Angola, eSwatini, Lesotho, Mauritius, Mozambique, South Africa
Blueberries
eSwatini, South Africa
Chicken
Angola, eSwatini, Lesotho, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa
Corn
Madagascar, Mauritius
Craft Beer
South Africa
Dairy Products
Madagascar, Mauritius, Zimbabwe
Table Eggs
South Africa
Food Ingredients
eSwatini, Mozambique, South Africa, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Table Grapes
Madagascar, Mauritius
Hops
Lesotho, Namibia, South Africa, Zimbabwe
Legumes
Zimbabwe
Plant and Animal Genetics
Botswana, eSwatini, Lesotho, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Plant Varieties
Zimbabwe
Pork
Madagascar, Mauritius, South Africa
Seafood
eSwatini, Lesotho, Madagascar, Mauritius, South Africa
Seeds
Mauritius (onion and potato), Zimbabwe (non-genetically modified)
Sorghum
Botswana, Lesotho, South Africa, Zimbabwe
Soybeans
eSwatini, Lesotho, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa
Turkey
Angola, South Africa
Whiskey
Angola, Botswana, eSwatini, Lesotho, Madagascar, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Wheat
Angola, eSwatini, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Zimbabwe
Wine
South Africa
Other Consumer-Oriented Products
Angola, Botswana, eSwatini, Lesotho, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Source: FAS/Pretoria and FAS GAIN report: U.S. and Southern Africa Agricultural Trade Reaches Record High
Across the Southern Africa region, there has recently been strong growth in imports of liquor (whiskey and bourbon), animal feed, plant and animal genetics, and consumer-oriented products. American whiskey sales to South Africa grew 17 percent from 2016 to 2017, reaching more than $10.5 million. Additionally, a decline in South Africa’s wine production and stocks may translate to new opportunities for U.S. wines despite a 25-percent import tariff. Similarly, U.S. apples from areas free of apple maggot (Rhagoletis pomonella), may see new opportunities in South Africa due to the severe drought in the Western Cape in 2017/2018, which will likely adversely impact domestic production.
With lifestyles and tastes around the world changing at an amazing speed, opportunities abound for expansion of U.S. agricultural products into emerging markets like those in Southern Africa. U.S. exporters offer high quality and variety and FAS is poised to assist with growing these markets and expanding the reach of U.S. agriculture.
Source link : https://fas.usda.gov/data/southern-africa-promising-region-us-agricultural-exports
Author :
Publish date : 2018-10-16 07:00:00
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.





